Why These Signs Mean You May Be Suffering From Liver Cancer – The liver, our powerhouse organ, performs a multitude of vital functions, from filtering toxins to producing essential proteins. When liver cells become abnormal and multiply uncontrollably, liver cancer, a potentially life-threatening condition, develops. While early detection holds significant promise for better outcomes, many individuals might not be aware of the subtle signs and symptoms in the initial stages. This article, informed by the latest research and expert insights, aims to empower you with knowledge about potential signs of liver cancer, its risk factors, and the importance of seeking timely medical attention.
Early Detection: Key to Improved Outcomes
Liver cancer initially often progresses silently, with symptoms manifesting only in later stages. Studies published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute highlight the significant impact of early detection on survival rates. A 2020 study reported that the five-year survival rate for individuals diagnosed at the earliest stage is promising. Nationally, only 26.6% of cases are diagnosed at an early stage when the five-year survival rate is much higher (63%). This underlines the crucial role of being informed about potential signs and symptoms and seeking medical evaluation if you experience any concerns.
Potential Signs and Symptoms:
It’s essential to remember that these signs and symptoms can also be caused by other health conditions. However, if you experience any of them, particularly for an extended period or with increasing intensity, consult your doctor to rule out any underlying issues, including liver cancer:
Early Stage:
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness or lack of energy, often unrelated to physical activity.
- Loss of appetite: A decrease in your usual food intake or disinterest in food.
Later Stage:
- Abdominal pain or swelling: Discomfort or bloating in the upper right abdomen, sometimes radiating to the right shoulder blade.
- Unexplained weight loss: Losing weight unintentionally without making any significant changes to your diet or exercise routine.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, indicating a buildup of bilirubin, a waste product normally processed by the liver.
- Dark urine: Urine appears darker than usual, potentially indicating problems with bile flow.
- Pale stools: Stool color lighter than usual, potentially signifying impaired liver function.
- Itching: This can be widespread or localized, often without an identifiable cause.
- Easy bleeding or bruising: Increased susceptibility to bleeding or bruising, even with minor injuries.
- Mental confusion: Difficulty thinking clearly, experiencing memory problems, or personality changes.
Remember: Early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. Don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice if you experience any of these symptoms, even if they seem mild or unrelated.
Common Risk Factors:
Understanding your risk factors can help you make informed lifestyle choices and prioritize regular health screenings. Here are some key risk factors for liver cancer:
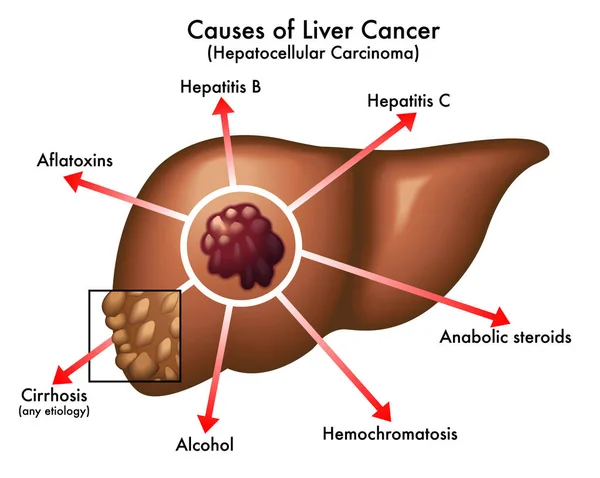
- Hepatitis B and C infections: Chronic infections with these viruses are major contributors to liver cancer development. Vaccination against hepatitis B and getting tested for hepatitis C are crucial preventive measures.
- Heavy alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake over time damages the liver, increasing the risk of cancer. Moderating alcohol consumption or abstaining altogether is recommended.
- Aflatoxin exposure: This toxin produced by mold on certain foods, like peanuts and corn, can be carcinogenic. Implementing proper food storage techniques and avoiding contaminated products is essential.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This buildup of fat in the liver, even without alcohol consumption, can progress to liver cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight and adopting a balanced diet are preventive strategies.
- Obesity: Excess body fat increases the risk of NAFLD and subsequently, liver cancer. Weight management through healthy eating and regular exercise is crucial.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the lungs and other organs, including the liver, increasing the risk of cancer. Quitting smoking is vital for overall health and cancer prevention.
- Family history: Having a close family member with liver cancer slightly increases your risk. Discussing your family history with your doctor is important.
Living with Liver Cancer:
A diagnosis of liver cancer can be overwhelming, but remember, you are not alone. With advancements in modern medicine, various treatment options like surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies are available. Each case is unique, and your doctor will develop a personalized treatment plan based on the stage and specific characteristics of your cancer.
Throughout your treatment journey, managing side effects and emotional well-being becomes crucial. Supportive care services, including pain management, nutritional counseling, and psychological support, play a vital role in improving your quality of life. Additionally, connecting with patient support groups or online communities can provide valuable peer support and understanding.
Prevention: Taking Control of Your Health:
While some risk factors like family history are not modifiable, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing liver cancer by adopting healthy lifestyle habits:
Empowering Strategies:
Here are evidence-based strategies you can implement to minimize your risk of liver cancer:
- Vaccination: Get vaccinated against hepatitis B, especially if you are at increased risk due to travel, occupation, or other factors. Talk to your doctor about the recommended schedule for vaccination.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Moderation is key. The American Cancer Society recommends no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men. Consider abstaining altogether if you have pre-existing liver conditions.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim for a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI) through a balanced diet and regular physical activity. Losing weight, even if you are not overweight, can significantly reduce your risk, especially if you have NAFLD.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Choose nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Limit processed foods, saturated and trans fats, and added sugar. Consider consulting a registered dietitian for personalized dietary guidance.
- Avoid Aflatoxin Exposure: Practice safe food handling and storage techniques. Opt for commercially prepared nuts and grains, and discard any moldy or discolored food products.
- Regular Checkups: Schedule regular checkups with your doctor, especially if you have any risk factors. This allows for early detection of any potential issues and prompt intervention.
- Manage Other Health Conditions: If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or other chronic conditions, managing them effectively can reduce your overall cancer risk, including liver cancer.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation is crucial for overall health and significantly reduces your risk of developing various cancers, including liver cancer. Seek support and resources to help you quit.
Remember: Prevention is always better than cure. By adopting these healthy lifestyle habits and staying informed about your health, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing liver cancer and live a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Beyond the Individual:
While individual efforts are crucial, broader public health initiatives are essential for effective liver cancer prevention. These include:
- Universal Hepatitis B Vaccination: Ensuring widespread access to and education about hepatitis B vaccination, particularly in regions with high prevalence, can significantly reduce the burden of liver cancer.
- Screening and Early Detection Programs: Implementing effective screening programs for high-risk individuals, particularly those with chronic hepatitis B or C infections, can facilitate early diagnosis and treatment, improving outcomes.
- Addressing Social Determinants of Health: Poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and unhealthy environments contribute to liver cancer risk. Addressing these social determinants through policy changes and community-based interventions is crucial for promoting health equity and reducing disparities in cancer outcomes.
Conclusion:
Liver cancer, while serious, is not a silent disease. By understanding the potential signs, risk factors, and effective preventive measures, you can empower yourself to take control of your health and reduce your risk. Remember, early detection is critical, so don’t hesitate to seek medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms. With advancements in medicine, comprehensive support systems, and a commitment to healthy living, individuals, and communities can work together to prevent liver cancer and create a healthier future for all.
Don’t Miss | What to Know About Computer Eye Strain: Protecting Your Vision in the Digital Age
Additional Resources:
- American Cancer Society: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/liver-cancer.html
- National Cancer Institute: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9662040/
- American Liver Foundation: https://liverfoundation.org/
- World Health Organization: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b
Note: This article is written based on scientific evidence found by the 247newsaroundtheworld.com team. Sources are duly referenced with keywords hyperlinked to source websites and are clickable for reference.