Diabetes symptoms in the body: Learn about warning signs like diabetic foot, fatigue, blurred vision, and more. Discover causes and tips to manage high blood sugar effectively.
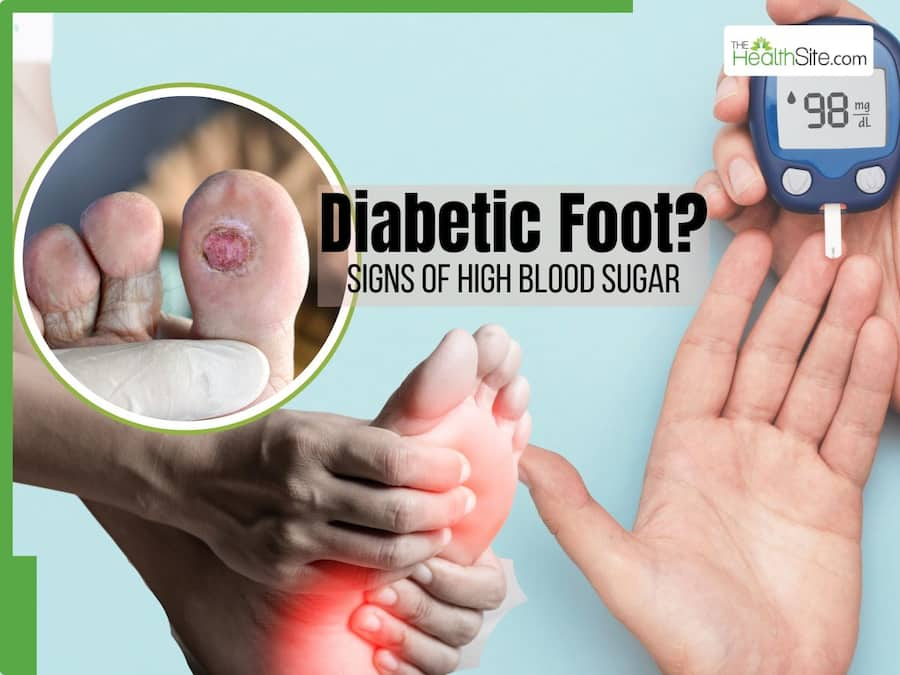
Signs of High Blood Sugar: Diabetes is a chronic health condition that is marked by uncontrolled high blood sugar levels. When the body is lacking insulin — the substance that helps convert glucose into energy, there are possibilities of excessive glucose accumulation in the blood — called high blood sugar. When someone leaves these high blood sugar levels, or hyperglycemia untreated for a long time, it can lead to various complications including kidney damage and heart attack. While the body may send a lot of signs with the onset of this condition, one of the most severe signs is the development of a diabetic foot, which may require medical intervention. Besides this, there are several other warning signs that your body may give when you are suffering from diabetes. In this article, we will give you a quick glimpse of all of them.
Warning Signs Your Body May Give When You Have Diabetes
High blood sugar occurs when the glucose levels in the bloodstream exceed normal ranges. This condition is often associated with diabetes but can also arise from stress, illness, or certain medications. Recognizing the signs early can prevent complications such as diabetic foot, cardiovascular issues, and nerve damage.
Diabetic Foot
One of the most alarming signs of high blood sugar is the development of diabetic foot. This condition arises due to nerve damage and poor blood circulation, which can lead to infections and, in severe cases, amputations. Regular foot examinations and maintaining blood sugar levels can help prevent this complication.
Frequent Urination
Frequent urination, or polyuria, is another common sign of high blood sugar. When glucose levels rise, the kidneys work overtime to filter and absorb the excess sugar. This process leads to increased urine production, which can result in dehydration and further complications if not managed properly.
Unusual Thirst
Alongside frequent urination, individuals may experience unusual thirst, known as polydipsia. This symptom occurs as the body attempts to replenish lost fluids due to excessive urination. Persistent thirst can be a warning sign of high blood sugar levels and should not be ignored.
Increased Hunger
Increased hunger, or polyphagia, is another sign that may indicate high blood sugar levels. When glucose is not effectively utilized by the body’s cells, it leads to a constant feeling of hunger. This can result in overeating, further exacerbating blood sugar issues.
Extreme Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom experienced by those with high blood sugar. When the body cannot effectively use glucose for energy, individuals may feel tired or lethargic. This lack of energy can impact daily activities and overall quality of life.
Blurry Vision
Blurred vision can also be a sign of high blood sugar levels. Elevated glucose can lead to swelling in the lenses of the eyes, affecting the ability to focus. This symptom can be temporary, but if high blood sugar persists, it may lead to more serious eye conditions.
Slow Healing
Slow healing of cuts and wounds is another concerning sign of high blood sugar. High glucose levels can impair the body’s natural healing processes, leading to prolonged recovery times. Individuals with diabetes are particularly susceptible to this issue, making regular monitoring essential.
Changes In Skin Texture
Changes in skin health can also indicate high blood sugar levels. Conditions such as dry skin, itching, or the development of dark patches may occur. These symptoms can signal insulin resistance or other metabolic issues and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
How to Manage High Blood Sugar Levels
Managing high blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical intervention. Regular monitoring of glucose levels, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in physical activity, and adhering to prescribed medications are essential steps. Consulting with healthcare providers can help individuals develop a personalized management plan.
Don’t Miss Out on the Latest Updates.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter Today!
Post source: The Health Site
Last Updated on January 27, 2025 by 247 News Around The World








