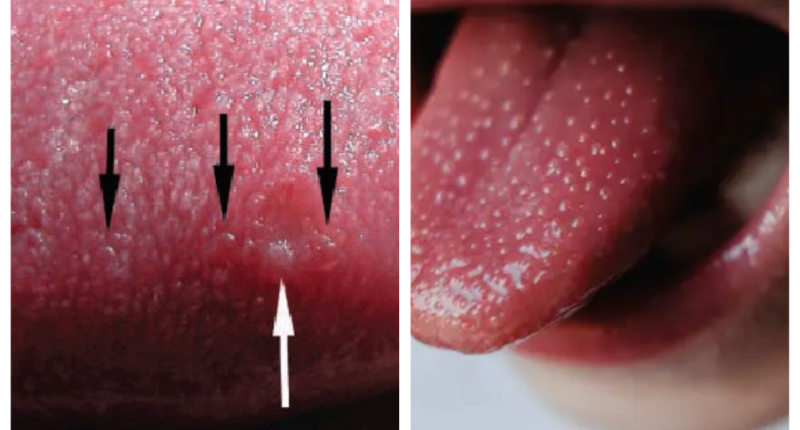
In the intricate landscape of oral health, one occasionally encounters the enigmatic condition known as Eruptive Lingual Papillitis Treatment. This peculiar ailment, characterized by the inflammation of fungiform papillae on the tongue, demands our attention for a comprehensive exploration of its symptoms, causes, and the nuances of its treatment. In this discourse, we delve into the intricate tapestry of this oral anomaly, offering insights into the diverse aspects of its management and preventive measures.
Understanding Eruptive Lingual Papillitis
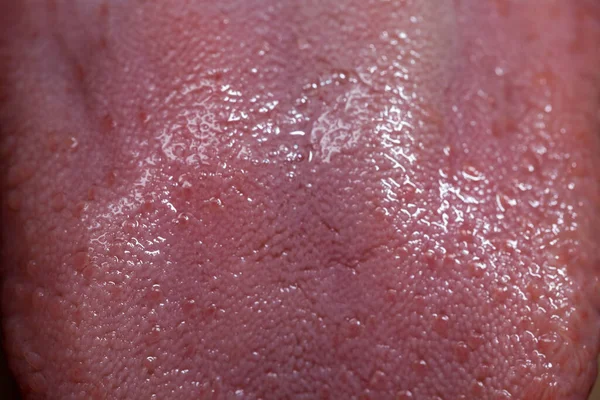
Symptoms Unveiled
To commence our exploration, it is imperative to unravel the distinctive symptoms that herald the presence of Eruptive Lingual Papillitis. Individuals grappling with this condition often report the emergence of small, painful bumps on the tongue. These bumps, accompanied by a heightened sensitivity, may render even routine activities such as speaking and eating discomforting.
The eruption of these papillae can also result in an increased sensation of heat on the tongue, further compounding the distress experienced by affected individuals. Notably, these symptoms may manifest abruptly, prompting an urgent need for diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Additional symptoms include:
- Eruptive lingual papillitis persists for more than two weeks
- Body temperature rises (fever)
- Soreness of the tongue
- Changes in the tongue colour (in large areas or in the form of dots of white, or red)
Diving into Causes
In the labyrinth of oral health intricacies, understanding the underlying causes of Eruptive Lingual Papillitis is paramount. While the precise etiology remains elusive in many cases, certain factors have been identified as potential catalysts for this condition.
- Viral Infections: It has been posited that viral infections, notably the Coxsackievirus, may be implicated in the onset of Eruptive Lingual Papillitis. This viral assailant can infiltrate the oral cavity, triggering an inflammatory response that manifests as the characteristic papillary eruption.
- Oral Hygiene Discrepancies: Inadequate oral hygiene practices have also been linked to the development of this condition. The accumulation of bacteria and debris on the tongue can provide a fertile ground for the eruption of papillae, underscoring the significance of vigilant oral care routines.
- Contact Irritants: Exposure to certain irritants, such as spicy foods or tobacco, may exacerbate the inflammation of lingual papillae. Sensitivities to these stimuli can heighten the discomfort experienced by individuals grappling with Eruptive Lingual Papillitis.
Additional Causes Include:
Eruptive lingual papillitis has an unknown exact cause. Inciting factors have been identified through research:
- Viruses can be causative agents.
- A diet high in sour, spicy, and sweet foods
- Chronic stress
- Chronic trauma to the tongue
- Gastrointestinal complications including constipation
- Allergic reactions
- Improper dental hygiene
- Smoking and frequent alcohol
The Art of Eruptive Lingual Papillitis Treatment
Having deciphered the intricacies of symptoms and causes, the crux of our discourse now shifts to the delicate art of Eruptive Lingual Papillitis Treatment. Navigating this terrain requires a multifaceted approach, addressing both symptomatic relief and the eradication of underlying causative factors.
After 2 or 3 days, the signs of temporary papillitis disappear on their own. However it is important to adhere to certain recommendations in order to avoid eruptive lingual papillitis.
1. Symptomatic Relief Measures
- Topical Analgesics: The application of topical analgesics can offer respite from the discomfort associated with Eruptive Lingual Papillitis. These formulations, often containing numbing agents, serve to alleviate pain and enhance the overall oral comfort of affected individuals.
- Oral Rinses: Gentle oral rinses, preferably with saline solutions, can assist in maintaining oral hygiene and mitigating inflammation. This uncomplicated yet effective measure contributes to the overall management of the condition.
2. Addressing Underlying Causes
- Antiviral Medications: In cases where viral infections are identified as contributing factors, the administration of antiviral medications becomes instrumental. This targeted approach aims to curtail the viral activity, thereby mitigating the inflammatory response.
- Optimizing Oral Hygiene Practices: Empowering individuals with knowledge about optimal oral hygiene practices is pivotal. Education on proper tongue cleaning techniques and the importance of regular dental check-ups can substantially diminish the recurrence of Eruptive Lingual Papillitis.
Additional Treatment Include:
Based on the diagnosis, the doctor will offer specific advice, but the recommended course of action may include: drug treatment.
- Antiviral drugs
- Antibiotics to treat bacterial overgrowth
- Antifungal agents to treat yeast overgrowth.
- Mouthwash medications
- Medications to increase saliva production
- Corticosteroids
Proactive Prevention
The aphorism “prevention is better than cure” holds true in the realm of oral health, and Eruptive Lingual Papillitis is no exception. Instilling preventive measures can significantly reduce the incidence and recurrence of this condition.
- Maintain Meticulous Oral Hygiene: The cornerstone of preventative care lies in meticulous oral hygiene. Regular brushing, flossing, and tongue cleaning form an indispensable trifecta in the defense against lingual papillary eruptions.
- Limit Exposure to Irritants: Recognizing and minimizing exposure to potential irritants, such as spicy foods and tobacco, serves as a preemptive strike against the development of Eruptive Lingual Papillitis. This conscious effort aligns with a holistic approach to oral well-being.
Additional
- Diet: Dentists suggest cutting less on hot and acidic meals. Avoid foods that are very spicy; all meals should be medium spicy.
- Using a paste and a brush, brush your teeth at least twice a day.
- It is preferable to clean the oral cavity after eating if the condition is severe.
- treatment of pulpitis, deep caries, and other dental diseases as soon as possible;
- Without entering the stage of complications, treatment of viral and 2 of the ENT organs and other tissues (tonsillitis, sinusitis, sinusitis; otitis media)
- The body receives enough nutrients, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, trace elements, and other helpful compounds.
- avoiding ingestion of poisonous substances that injure the gums and dental enamel (lemonade, coffee, strong tea)
- kicking harmful behaviours to the curb (alcohol, smoking)
Conclusion: Navigating the Terrain of Eruptive Lingual Papillitis
In the labyrinth of oral health intricacies, Eruptive Lingual Papillitis emerges as a distinctive and occasionally perplexing entity. Armed with a comprehensive understanding of its symptoms, causes, and treatment modalities, individuals can navigate this terrain with informed resilience.
The treatment landscape, marked by symptomatic relief measures and targeted interventions, underscores the nuanced approach required to address Eruptive Lingual Papillitis. Moreover, the proactive embrace of preventative measures propels us toward a future where the occurrence of this condition becomes a rarity rather than a commonplace concern.
As we conclude our exploration, let us acknowledge the imperative of disseminating knowledge and fostering a culture of oral health awareness. In doing so, we fortify our collective defenses against the enigmatic nuances of conditions such as Eruptive Lingual Papillitis.
Note: This article is written based on scientific evidence found by the 247newsroundtheworld.com team. Sources are duly referenced with keywords hyperlinked to source websites and are clickable for reference.
Last Updated on February 18, 2025 by 247 News Around The World