Not all blemishes are alike, and an effective treatment plan for any skin issue requires a proper diagnosis. Fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis or malassezia folliculitis, is a common skin condition that occurs when a type of yeast called Malassezia overgrows in the hair follicles. This can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Small, red or white bumps
- Itching
- Burning
- Scaling
- Pustules
Fungal acne is often mistaken for bacterial acne, but it is important to see a doctor to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Treatment for fungal acne typically involves topical or oral antifungal medications. Topical antifungal medications, such as ketoconazole, clotrimazole, or miconazole, are usually applied to the affected areas once or twice a day for two to four weeks. Oral antifungal medications, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, are typically taken for one to two weeks.
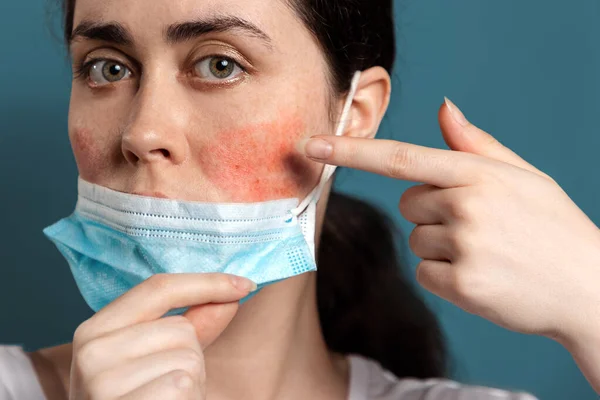
What Is Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne, akin to more common types of acne, is a skin condition triggered by a particular type of infection. The culprit, in this case, is Malassezia, a yeast-like fungus naturally present in human skin. Normally, the body effectively regulates the levels of this fungus. However, persistent skin dampness creates an environment conducive to fungal multiplication. Gradually, Malassezia infiltrates hair follicles, prompting an immune response that includes inflammation and the mobilization of white blood cells. This ongoing battle for skin health becomes evident through the formation of small bumps resembling acne vulgaris on the skin.
Diverging Paths: Fungal Acne vs. Acne Vulgaris
Discerning Differences
While the visual semblance between fungal acne and acne vulgaris is striking, nuances in their etiology set them apart. Acne vulgaris is rooted in the overactivity of sebaceous glands and the subsequent colonization by Propionibacterium acnes. On the contrary, fungal acne pivots on the overgrowth of Malassezia yeast.
Diagnostic Challenges
Given their visual overlap, distinguishing between the two can be challenging. Dermatologists often resort to diagnostic tools like skin scrapings or cultures to pinpoint the causative agent. Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatments, emphasizing the importance of clarity in identification.
Causes of Fungal Acne
- Increased oil production
- Warm, humid conditions
- Weak immune system
- Certain medications, such as oral contraceptives and corticosteroids
Fungal Acne Treatment Options
Because Malassezia exists naturally on your skin, the goal of treatment is to restore healthy levels of the fungus. Your dermatologist may recommend an oral or topical anti-fungal medication. Research is showing some success with photodynamic light therapy, although this is reserved for more complex cases of fungal acne and for patients who experience side effects from medication.
Treatment for fungal acne:
- Topical antifungal medications, such as ketoconazole, clotrimazole, or miconazole
- Oral antifungal medications, such as fluconazole or itraconazole
- Gentle skincare routine
- Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding harsh soaps and scrubs, not picking or popping pimples, and keeping skin clean and dry
How Long Does Fungal Acne Treatment Take?
Most patients will need to use the medications as prescribed by their dermatologist, even if their skin improves. On average, it takes up to one month to balance the flora on your skin and for most blemishes to be cleared away. Sometimes several months of treatment are necessary.
The Prevention Game: Strategies for Clear Skin
Preventing fungal acne involves a multi-faceted approach. Here are essential tips to keep this pesky condition at bay:
- Wash your face twice a day with a gentle cleanser.
- Use a mild dandruff shampoo to wash your hair two to three times a week.
- Avoid harsh soaps and scrubs.
- Do not pick or pop pimples.
- Keep your skin clean and dry.
- Avoid hot showers and baths.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing.
Beyond Skin Deep
Psychological Impacts
The impact of fungal acne extends beyond the physical realm, infiltrating the psychological landscape. Unraveling the emotional toll is integral in devising a comprehensive Fungal Acne Treatment strategy. Empathy, coupled with dermatological expertise, forms the crux of patient-centered care.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Navigating the intricate terrain of fungal acne warrants professional guidance. Dermatologists, equipped with diagnostic acumen, tailor treatment plans to individual profiles. The symbiosis of medical expertise and patient compliance propels the journey toward resolution.
Conclusion: Nurturing Skin Health
In the intricate tapestry of dermatological challenges, fungal acne emerges as a distinctive thread. The journey from symptoms to prevention, differentiating it from its ubiquitous counterpart, demands meticulous attention. Armed with knowledge and a tailored Fungal Acne Treatment strategy, individuals can navigate this dermatological labyrinth, fostering skin health and well-being.
Note: This article is written based on scientific evidence found by the 247newsroundtheworld.com team. Sources are duly referenced with keywords hyperlinked to source websites and are clickable for reference.